Image math
|
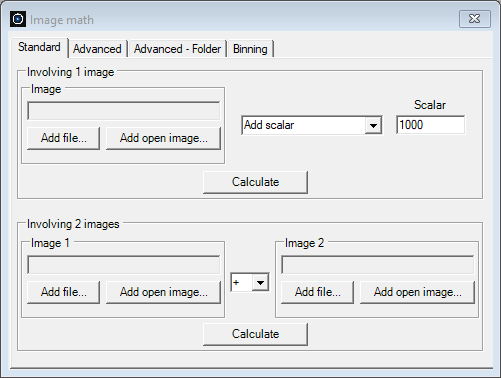
The Image Math dialog box provides a range of image processing operations that can be applied to either a single FITS image or multiple FITS images. It is organized into following tabs: Standard, Advanced, Advanced - Folder and Binning, each of which is detailed in the following sections. Standard The Standard tab consists of two sections: Involving 1 image, Involving 2 images.
Click the Calculate button to execute the operation. The resulting image will open in a new FITS window.
Click the Calculate button to execute the operation and display the resulting new FITS image. Advanced The operations in this tab allow to combine multiple FITS images. One has to keep in mind that all FITS images recorded by a sensor include noise. When performing operations such as addition or subtraction of images, the noise accumulates. This observation is particularly significant in the image calibration process, elucidating why the standard practice involves utilizing multiple bias, dark and flat frames to calibrate a Science image, rather than relying on a single frame of each type. By first averaging multiple bias, dark and flat frames before applying them to a Science image, the introduction of noise is significantly curtailed. The Advanced tab provides operators designed for large sets of FITS images, enabling actions such as averaging or median combining the set to produce a new image.
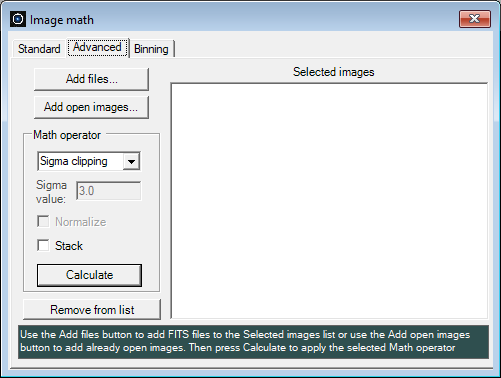
The Advanced tab necessitates a minimum of two FITS images, which can be acquired by either opening FITS files using the Add files option or by selecting already open FITS images through the Add open images option. Once the files or open images are selected, the Selected images box will display the chosen entries. Subsequently, choose an operator from the Math operator section. Utilize the drop down list to select the desired operator:
The Stack option is a feature compatible with all 4 previously mentioned methods. It is particularly useful in situations involving a series of images capturing the same target but exhibiting slight variations, i.e. shifts in the x-y plane caused by a minor movement of the field of view (e.g., resulting from imprecisions in the telescope mount tracking). The stack operation helps to improve the SNR ratio of your image: when enabled, each image undergoes x-y shifting relative to the first image, employing a cross-correlation technique, to ensure that all pixels align spatially. The first image remains unaltered, serving as a reference image to which all subsequent images are aligned. After stacking, the chosen operator (e.g., average or median combine) is then applied. The Normalize option is available when selecting the Average or Median methods. When enabled, each image undergoes a median-normalization before the selected operator (e.g., average or median combine) is employed. Median-normalization entails determining the median value of an image, and subsequently dividing each pixel value of the image by this median value. Normalization is commonly applied when working with flat field frames. Each flat field image is normalized (adjusted) to values approximating unity. This ensures that post flat field correction, the numerical intensities in the images resemble those prior to flat fielding. In simpler terms, the flat field correction for pixels with responses close to the median is adjusted to approximately 1. Use the Remove from list button to remove one or more entries from the Selected images list. Advanced - Folder
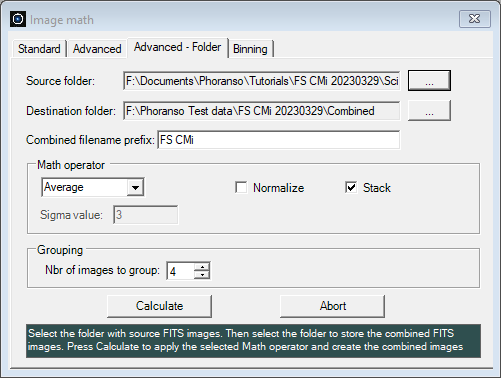
The Advanced - Folder tab processes a Source folder of FITS images, combining them using the selected Math operator to produce new combined FITS images, which are saved in the designated Destination folder. Example Use Case First select the Source folder containing the images to combine. Then specify the Destination folder, where the combined images will be saved. Phoranso automatically generates filenames for the combined files, based on the selected options. Each file also includes a unique sequence number. In the above example, the first combined file will be named: FS CMi_StackedImage_Average_0001.fit:
The Math operator section includes the following fields:
The Grouping section allows to specify the number of Source folder images to each time combine into a single, grouped image image.
To initiate the process, click the Calculate button. If needed, you can stop the process at any time by clicking Abort. Binning The operations in this tab allow to bin one or more FITS images. Binning is the process of combining adjacent pixels into a single (super) pixel, often in a square grid format (i.e., 2x2, 3x3, etc). Example: when you bin an image 2x2, Phoranso combines 4 pixels into a single pixel, halving the image resolution in each dimension.
First add one or more FITS images to the Selected images list using the Add files or Add open images buttons. Next, select the desired Binning operator from the drop down list (options are 2x2, 3x3 and 4x4 binning) and the Pixel combination to be applied. Press Calculate to start the binning operation, which results in the display of one new binned image for each image in the list of Selected images.
Use the Remove from list button to remove one or more entries from the Selected images list. |
|
|